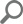What is Basel II
The Basel Capital Accord Basel II a set of international banking standards based on three mutually reinforcing pillars, issued by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision in June 2004. It’s an improvement of the Basel I Accord, and it introduces a new approach to data management
Pillar 1 – minimum capital requirements – defines the minimum capital required to cover the risks that the bank might encounter. To put it simply – the financial institutions are required to have enough cash to cover potential risks.
Pillar 2 – supervisory review – is designed to strengthen and reinforce the role of supervisors that guarantee the effectiveness of Basel II. According to IMF “Banks have a process for assessing capital adequacy (CAAP) and a strategy for maintaining capital level. Supervisors evaluate banks’ internal capital adequacy systems and compliance. Higher capital adequacy levels for individual banks if risk profile requires. Early intervention by supervisors. Stress tests and Assessment of interest rate risk and concentration risk.” [1]
IMF defines the following as Pillar 2 key requirements:
“Supervisory ability and capacity to make the necessary assessments.
Adequate legal and regulatory framework to take action.” [1]
Pillar 3 – market discipline – “The Committee aims to encourage market discipline by developing a set of disclosure requirements which will allow market participants to assess key pieces of information on the scope of application, capital, risk exposures, risk assessment processes, and hence the capital adequacy of the institution.” [2]
IMF defines the following as Pillar 3 key requirements:
“Banks’ information systems to produce required breakdowns;
Accounting and auditing systems that safeguard accuracy of disclosures; and
Ability to require disclosure, monitor and verify.” [1]
Who has to comply with Basel II?
Basel II is an international act and a large number of countries have adopted it for their banking systems. It applies to internationally active banks and financial entities, and affects retail banking, commercial banking, payments and settlements, corporate finance, asset management, trading, sales, and retail brokerage.
What is Basel II meant to ensure?
The goals of Basel II are providing stabile, safe and sound financial systems, based on accurate data, consistency and control.
How is Basel II compliance checked?
National supervisors audit and guarantee the effectiveness of Basel II. The audit frequency depends on the financial health of the bank audited. The banks with better financial situation shown in the last audit are audited less frequently than the banks with lower financial rating.
Complying with Basel II requires controlled systems, accurate reporting in a timely manner, and information security. It also requires handling internal and external fraud (preventing unauthorized activity, documenting access and activity), information theft, sensitive data leak, and other system security incidents.
ApexSQL Audit helps as it:
- Automatically audits events that can have significant business impact
- Provides accurate and timely reports for compliance reviews
- Provides reports that discover data security risks
- Identifies compliance and security vulnerabilities
Reporting
Although the Basel II Accord doesn’t explicitly mention requirements for IT departments, environment standards and database rules, it’s clear that the accuracy of the information requested for a supervisory review can be fulfilled only in a strictly controlled and monitored system.
The ApexSQL Audit reports that can help protect bank’s IT systems and maintain an efficient information security policy are:
The Audit settings history report shows all changes to the SQL Server instance and database auditing settings:
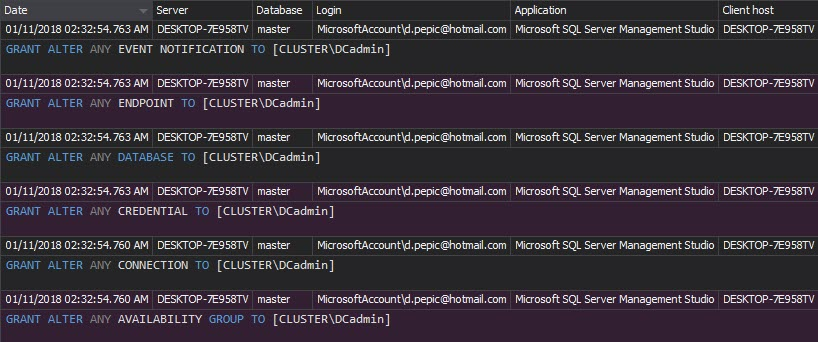
The Security configuration history report – shows all changes in permission settings for SQL Server security entities. Once the security parameters for SQL Server users, logins, and roles are set, any undocumented change in the permissions is a potential threat:
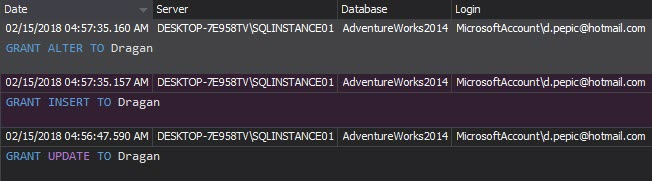
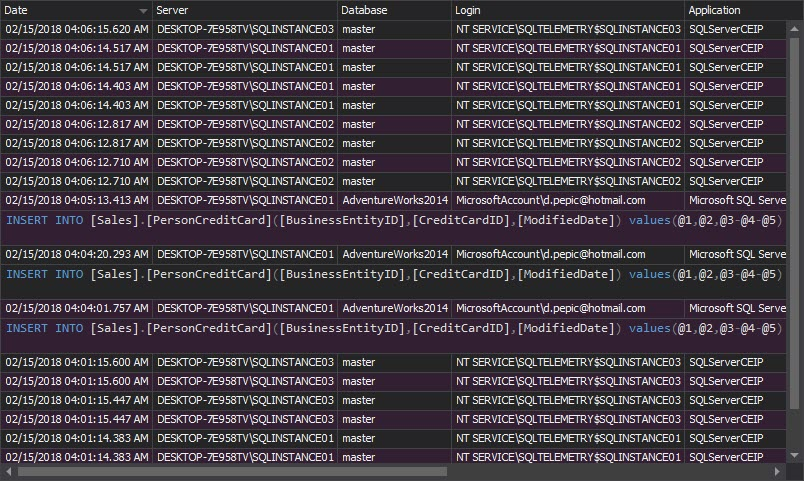
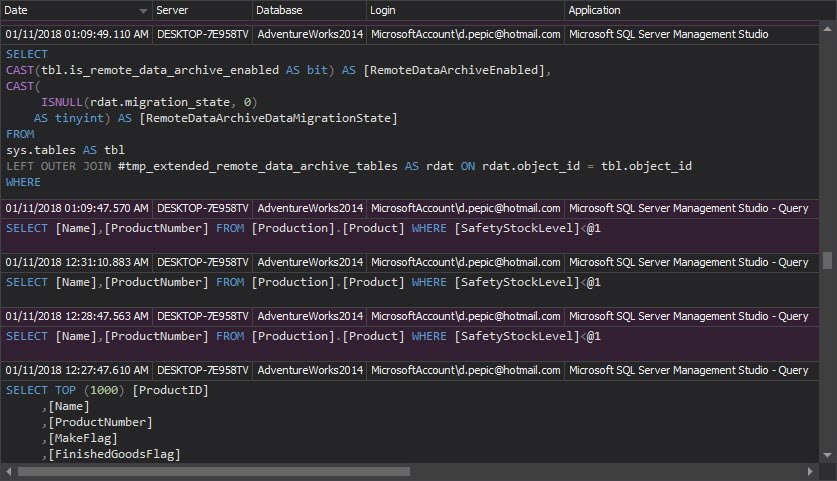
The Complete audit trail report shows all events logged on audited SQL Server instances. The report is not necessary for every day analysis, but is useful for occasional deeper investigation of what’s going on
The Access history report shows who and when accessed a specific object:
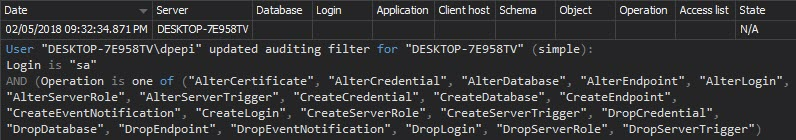
The Permission changes report shows the permission changes for a specific user or object. If the permissions are granted without required documentation, they should be investigated and probably denied, as they can lead to security problems:
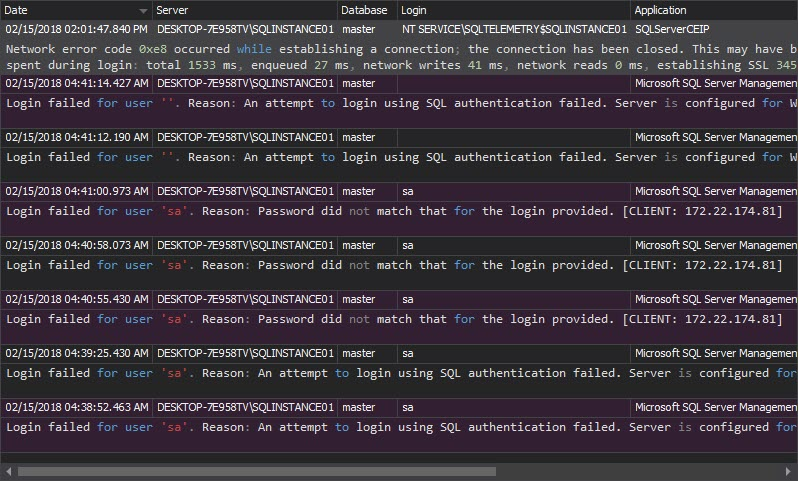
The Unauthorized access report shows all failed login attempts made by non-existing users or existing users with wrong passwords:
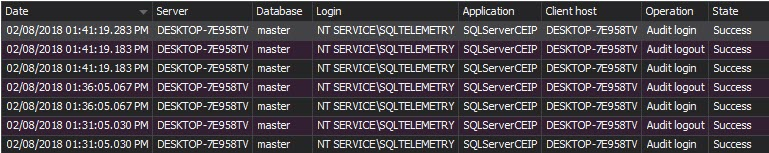
The Logon activity history report shows the information about failed and successful login attempts on a specific SQL Server instance:
When it comes to your databases, compliance with Basel II is achieved through event auditing, regular reporting and strict security rules. Permissions granted to users should be minimal needed. Use ApexSQL Audit to audit your SQL Server instances and databases and to identify potential security threats
References:
[1] Implementation of Basel II—Implications for the World Bank and the IMF
[2] From Basel I to Basel Ii: An Analysis of The Three Pillars
Useful resources
International Monetary Fund – Implementation of Basel II—Implications for the World Bank and the IMF
Federation of American Scientists: U.S. Implementation of the Basel Capital Regulatory Framework
Bank for International Settlements: Basel II implementation in the United States
October 16, 2013