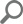This article explains different ways to export MySQL data to JSON file format. JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation. It is a lightweight file format for storing and transferring data, commonly used when data is sent from a server to a web page.
In the first section of the article, we will take a look at some MySQL functions as one solution for exporting MySQL data to JSON. Next, we will see how MySQL Shell and JSON output functions can be used to achieve the same goal, and last but not least, we will get familiar with an extension, ApexSQL Database Power Tools for VS Code and its Export to JSON feature.
The following method for exporting will be used:
- CONCAT() and GROUP_CONCAT() functions
- JSON_OBJECT and JSON_ARRAYAGG functions
- MySQL Shell and JSON Format Output
- Export to JSON using a third-party software
For this article, the SQL code below will be used as an example:
CREATE DATABASE addresses; USE addresses; CREATE TABLE location ( address_id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, address varchar(50) NOT NULL, address2 varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (address_id) ); INSERT INTO location VALUES (NULL, '1586 Guaruj Place', '47 MySakila Drive'), (NULL, '934 San Felipe de Puerto Plata Street', NULL), (NULL, '360 Toulouse Parkway', '270, Toulon Boulevard');
(source: How to export MySQL data to CSV)
Exporting MySQL data to JSON using the CONCAT() and GROUP_CONCAT() functions
Using a combination of CONCAT() and GROUP_CONCAT() functions, data from SQL string can be converted into JSON format.
In a query editor, execute the following code:
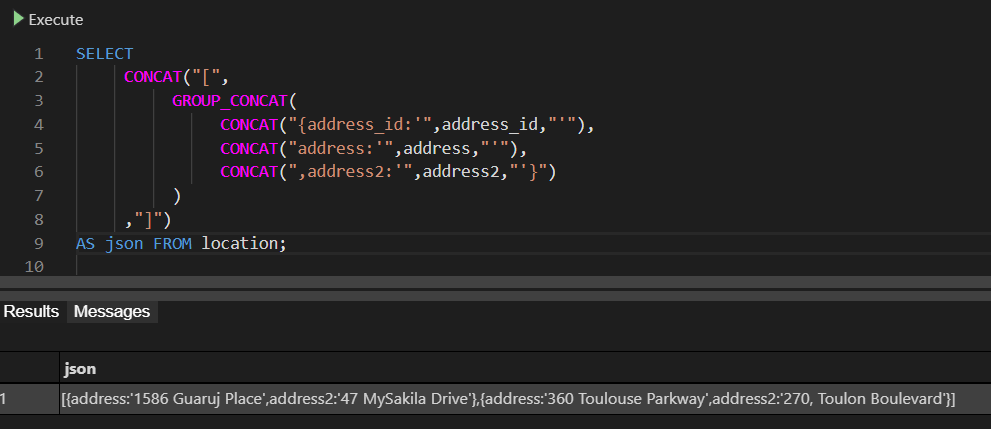
SELECT CONCAT("[", GROUP_CONCAT( CONCAT("{address_id:'",address_id,"'"), CONCAT("address:'",address,"'"), CONCAT(",address2:'",address2,"'}") ) ,"]") AS json FROM location;
The results will be something like this:
[{address_id:’1’address:’1586 Guaruj Place’,address2:’47 MySakila Drive’},{address_id:’3’address:’360 Toulouse Parkway’,address2:’270, Toulon Boulevard’}]
To export these results from query result to a JSON file, add one more line of code:
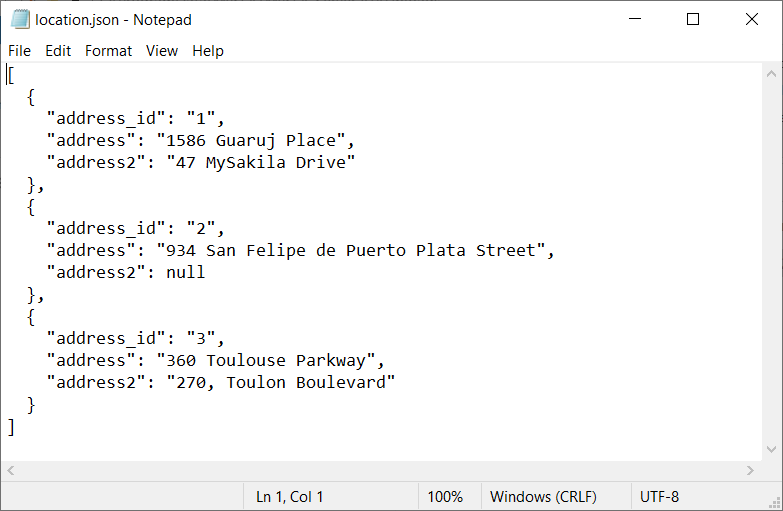
SELECT CONCAT("[", GROUP_CONCAT( CONCAT("{address_id:'",address_id,"'"), CONCAT("address:'",address,"'"), CONCAT(",address2:'",address2,"'}") ) ,"]") AS json FROM location INTO OUTFILE 'C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads/location.json'
After executing, the result will be similar like in the image below:
- More about the usage of INTO OUTFILE can be found in the How to export MySQL data to CSV article.
Exporting MySQL data to JSON using JSON_OBJECT and JSON_ARRAYAGG functions
The JSON_OBJECT function maps a variable number of arguments to a JSON object. It creates a list of key-value pairs and returns a JSON object containing those pairs. By providing each key/value pair as two separate arguments. Each pair becomes a key/value pair in the resulting JSON object.
When the code below is executed:
SELECT JSON_OBJECT ('address_id', address_id, 'address', address, 'address2', address2) FROM location;
The results should be something like this:
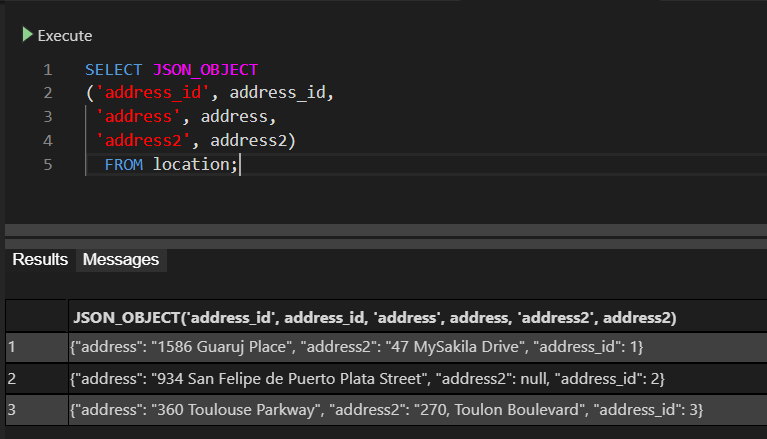
Now, let’s modify the code to export data to a JSON file. Execute the following:
SELECT JSON_OBJECT ('address_id', address_id, 'address', address, 'address2', address2) FROM location INTO OUTFILE 'C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads/location.json'
When the newly created JSON file is opened, the results will look like this:
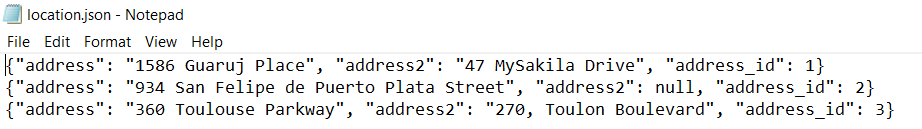
If you want the results set to be as one row containing a JSON array with one object per row, then the JSON_ARRAYAGG function should be used in combination with the JSON_OBJECT function. Each row of the result set ends up as a single element in the array.
Execute the result below to see results:
SELECT JSON_ARRAYAGG(JSON_OBJECT ('address_id', address_id, 'address', address, 'address2', address2)) FROM location
Add the INTO OUTFILE command to export MySQL data to JSON file:
SELECT JSON_ARRAYAGG(JSON_OBJECT ('address_id', address_id, 'address', address, 'address2', address2)) FROM location INTO OUTFILE 'C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads/location.json';
- Note: The JSON_ARRAYAGG function is available from the MySQL server 8.0 version.
Export MySQL data to JSON using MySQL Shell and JSON Format Output
MySQL Shell provides several JSON format options to print result sets:
- json – returns the JSON values in a nicely formatted way, which makes it easier for humans to read
- ndjson – returns raw JSON delimited by newlines
- json/array – returns raw JSON wrapped in a JSON array
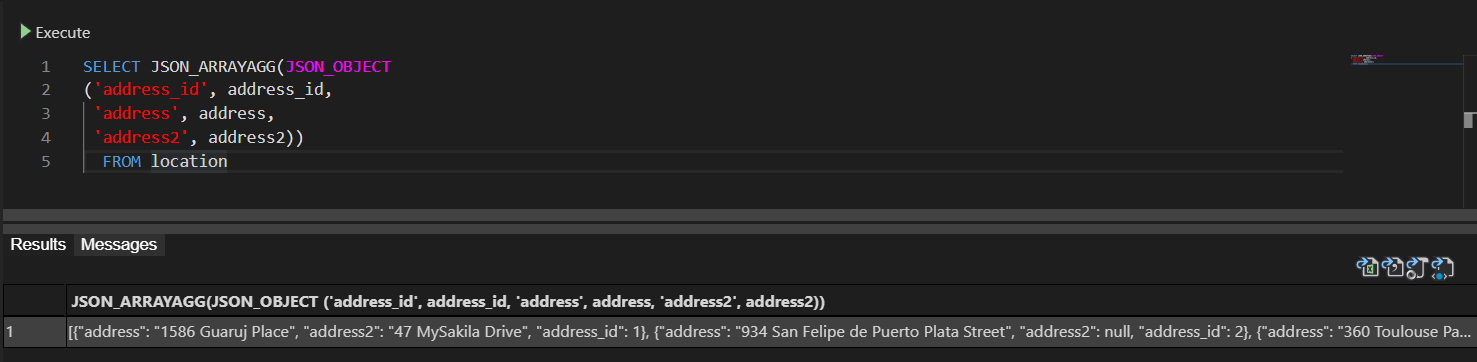
Start MySQL Shell and connect to a database from which you want to export data:
To connect to a database, in MySQL Shell execute the following command:
\connect root@localhost:33060/addresses
The json output file format
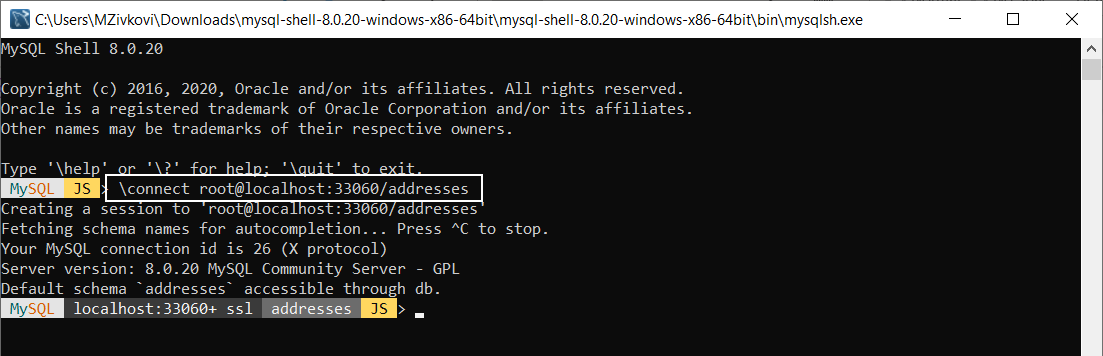
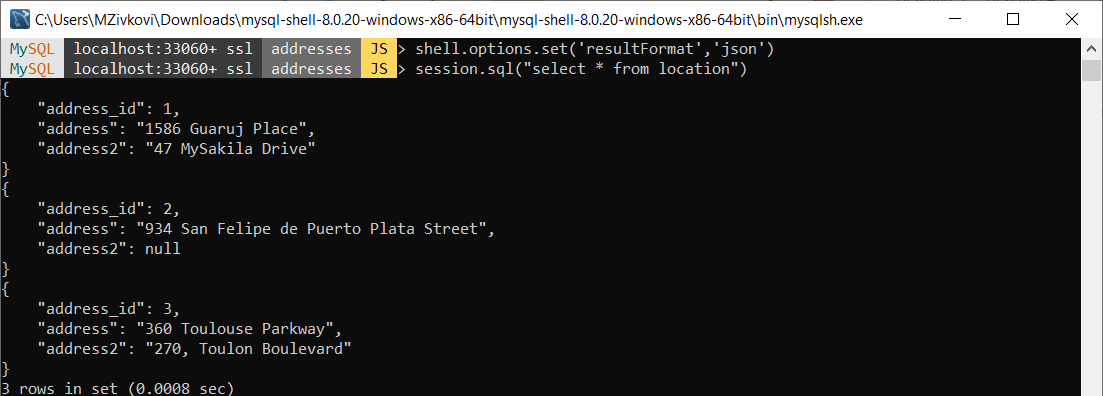
To format data values in the json output, in MySQL Shell execute the following code:
shell.options.set('resultFormat','json')
After that, execute the following code to pull data from the location table:
session.sql("select * from location")
The output will look something like this:
- {
- “address_id”: 1,
- “address”: “1586 Guaruj Place”,
- “address2”: “47 MySakila Drive”
- }
- {
- “address_id”: 2,
- “address”: “934 San Felipe de Puerto Plata Street”,
- “address2”: null
- }
- {
- “address_id”: 3,
- “address”: “360 Toulouse Parkway”,
- “address2”: “270, Toulon Boulevard”
- }
The ndjson output file format
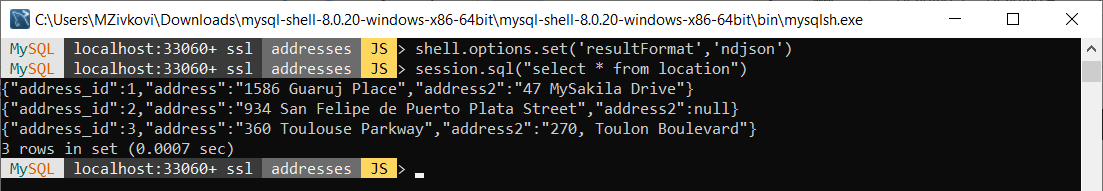
In the MySQL Shell, execute the following code to change the result format:
shell.options.set('resultFormat','ndjson')
Now, when the code is executed:
session.sql("select * from location")
Results will be like this:
{“address_id”:1,”address”:”1586 Guaruj Place”,”address2″:”47 MySakila Drive”}
{“address_id”:2,”address”:”934 San Felipe de Puerto Plata Street”,”address2″:null}
{“address_id”:3,”address”:”360 Toulouse Parkway”,”address2″:”270, Toulon Boulevard”}
The json/array output file format
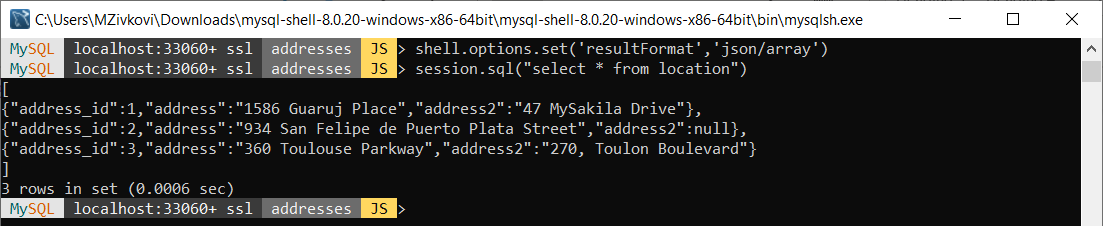
To switch to json/array result format, in MySQL Shell execute the code below:
shell.options.set('resultFormat','json/array')
Now, when a SELECT statement is executed, the output will look like this:
[
{“address_id”:1,”address”:”1586 Guaruj Place”,”address2″:”47 MySakila Drive”},
{“address_id”:2,”address”:”934 San Felipe de Puerto Plata Street”,”address2″:null},
{“address_id”:3,”address”:”360 Toulouse Parkway”,”address2″:”270, Toulon Boulevard”}
]
Exporting MySQL data using third-party software
ApexSQL Database Power Tools for VS Code is an extension that can export data from the results grid into a JSON file format in just a few steps. Beside JSON, the extension has options to export MySQL data to CSV, Excel, and HTML file format.
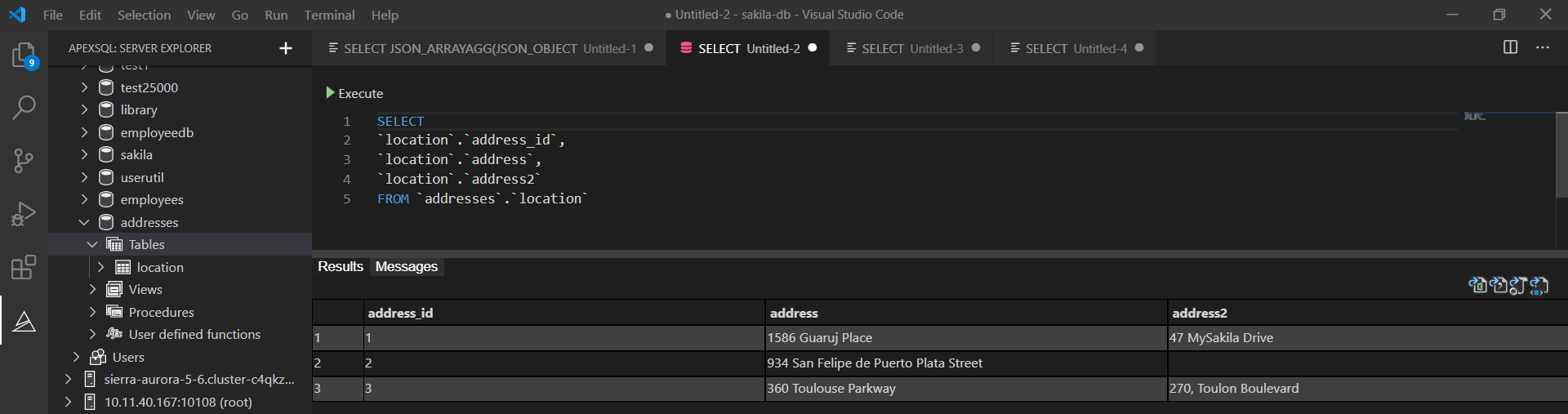
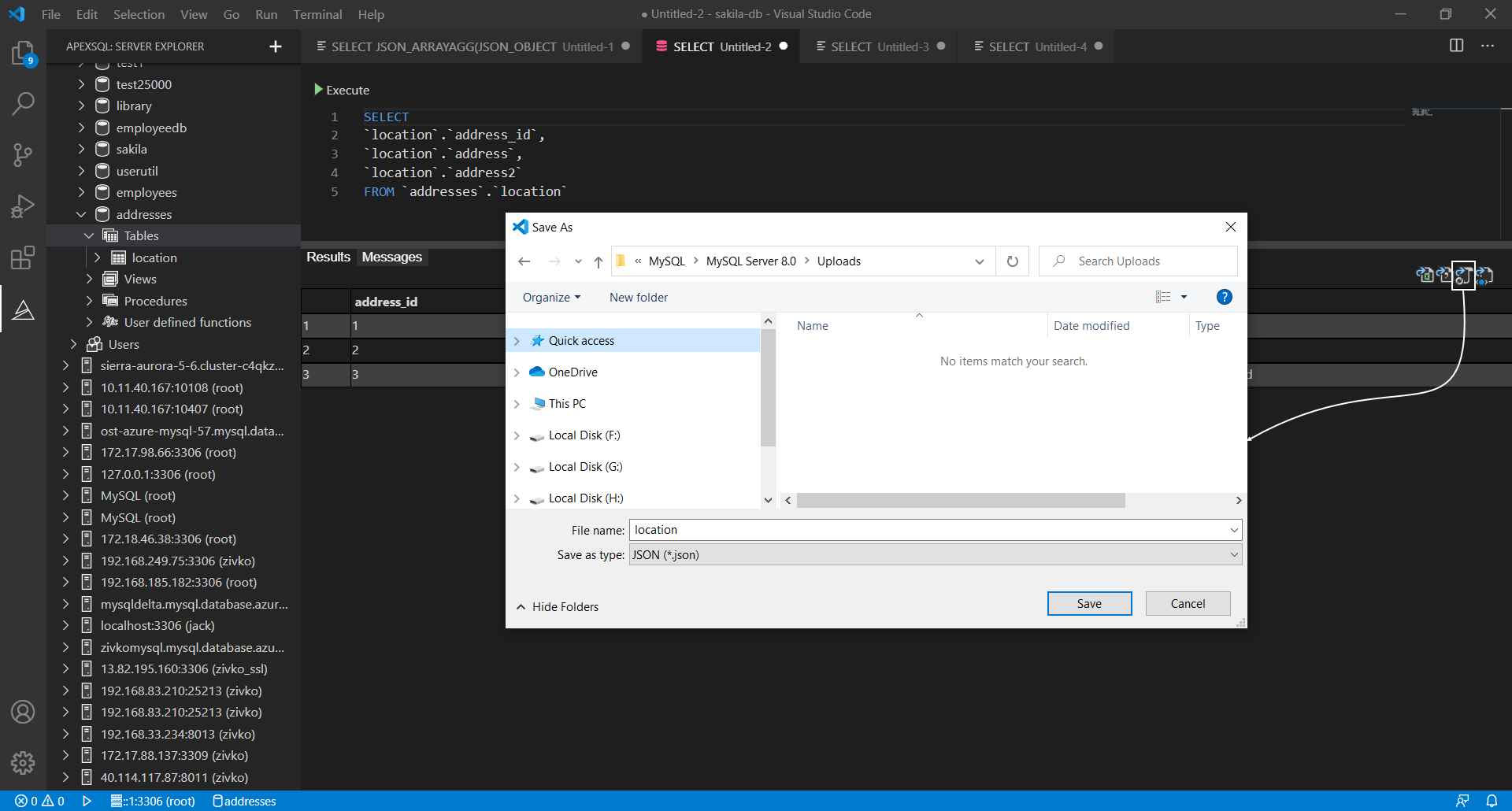
To export data, in Visual Studio Code under the ApexSQL server explorer pane, open a new query:
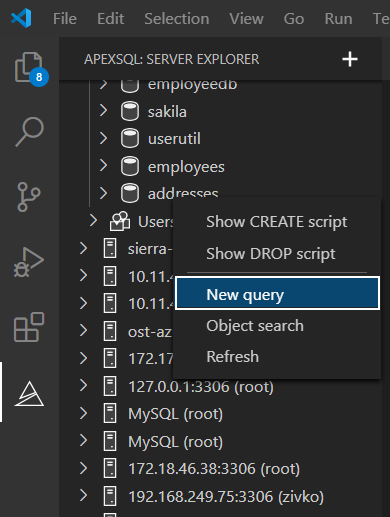
In a newly opened query editor, execute a SELECT statement from which you want the results to be exported:
On the top right corner of the results grid, click the Export to JSON icon. In the Save As window, choose a location for export MySQL data to JSON file, under the File name enter a name for the file and click the Save button:
After the file is saved, on the application bottom right corner, an info message appears with the Show button. When clicked on it, it will open up the location where the file is saved:
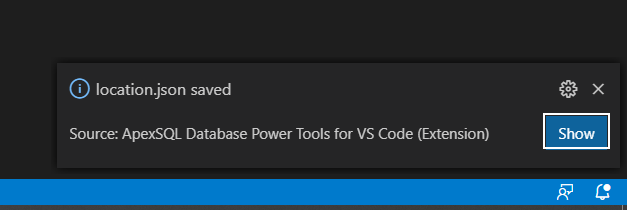
Newly saved data will look like this:
July 23, 2020